Views: 222 Author: Astin Publish Time: 2024-10-27 Origin: Site








Content Menu
● Technical Specifications and Design
● Modern Adaptations and Civilian Use
● Maintenance and Safety Considerations
>> 1. What is the maximum span length of a standard Bailey bridge?
>> 2. How long does it typically take to construct a Bailey bridge?
>> 3. What are the main advantages of Bailey bridges over conventional bridges?
>> 4. Can Bailey bridges be used in extreme weather conditions?
>> 5. What is the typical lifespan of a Bailey bridge?
The Bailey bridge stands as one of the most significant military engineering innovations of the 20th century, revolutionizing tactical mobility and strategic operations. Developed during World War II, this portable, pre-fabricated truss bridge system has become an indispensable tool in military engineering and civil applications alike. Its significance was so profound that Field Marshal Montgomery famously declared that "without the Bailey bridge, we should not have won the war". The bridge's versatility, ease of assembly, and robust design have made it an essential component of military infrastructure, enabling rapid deployment and strategic advantage in various combat scenarios.
The Bailey bridge was invented by British civil engineer Sir Donald Coleman Bailey in 1940-1941 while working at the Experimental Bridging Establishment. Born in Rotherham in 1901, Bailey's engineering background in railway bridge design proved instrumental in developing this revolutionary bridge system. The bridge was designed to address the critical need for a portable, easily assembled bridge that could support heavy military vehicles and equipment. The invention came at a crucial time during World War II when the Allied forces needed a reliable method to cross rivers and ravines, particularly during the advance through Europe. The design was so successful that by the end of the war, the British, Canadian, and American forces had constructed numerous Bailey bridges across Europe, facilitating their advancement and ultimately contributing to the Allied victory.

The Bailey bridge's genius lies in its modular design and simple components. The bridge consists of three main elements: panels, transoms, and stringers. The panels form the bridge's main structure, while transoms are the cross-beams that support the deck, and stringers run lengthwise to distribute the load. Each component is designed to be light enough to be carried by a small group of soldiers, yet when assembled, the bridge can support substantial military loads. The standard panels are 10 feet long and can be combined in various configurations to achieve different span lengths and load capacities. The bridge can be assembled in single-story, double-story, or triple-story configurations, with additional reinforcement possible through multiple parallel trusses. This flexibility allows for spans of up to 200 feet and load capacities sufficient for heavy tanks and military vehicles.
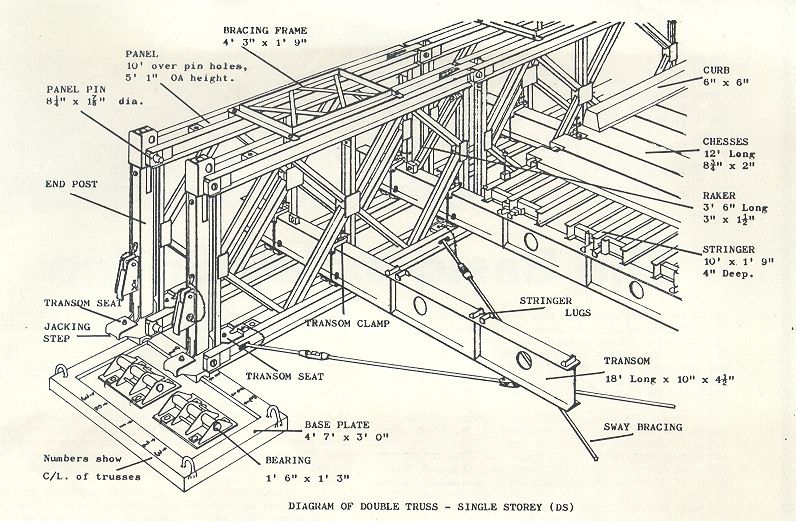
The construction of a Bailey bridge is a testament to military engineering efficiency. The process begins with site preparation and the assembly of a launching nose, which helps counterbalance the bridge during construction. The bridge is typically built on rollers on one bank and pushed across the gap to the other side. This method, known as the cantilever launch method, allows for safe assembly without requiring access to the far bank. The construction process involves systematically adding panels, transoms, and decking while maintaining proper alignment and balance. What makes the Bailey bridge particularly remarkable is that it requires no specialized tools or heavy equipment for assembly, making it ideal for rapid deployment in combat situations. A skilled team can construct a standard Bailey bridge in a matter of hours, depending on the span length and configuration required.
In military operations, the Bailey bridge serves multiple critical functions. It enables rapid movement of troops and equipment across obstacles, facilitates supply lines, and supports combat engineering operations. The bridge's versatility allows it to be used in various tactical situations, from temporary river crossings to semi-permanent infrastructure replacement. Its modular design means it can be strengthened or modified as needed to accommodate different load requirements or span lengths. The bridge has proven invaluable in both combat and humanitarian operations, demonstrating its utility in disaster relief and emergency response situations. Modern military forces continue to rely on Bailey bridge principles, with contemporary variants incorporating advanced materials and design improvements while maintaining the original's fundamental simplicity and effectiveness.
The success of the Bailey bridge in military applications has led to its widespread adoption in civilian infrastructure projects. Modern versions of the Bailey bridge are used in emergency bridge replacement, temporary traffic diversions during construction, and disaster relief operations. The design has been adapted to meet current safety standards and civilian load requirements while maintaining the original's quick assembly and reliability principles. Commercial variants often feature improved corrosion protection, enhanced deck systems, and modifications for specific applications such as pedestrian bridges or heavy industrial use.
Maintaining a Bailey bridge requires regular inspection and attention to key components. Critical areas include the panel connections, decking condition, and foundation stability. Safety protocols during both construction and use are essential, with particular attention paid to proper assembly procedures, load limits, and weather conditions. Modern Bailey bridges incorporate various safety features and are subject to strict engineering standards to ensure reliable performance under diverse conditions.
The future of Bailey bridge technology continues to evolve with advances in materials science and engineering. Modern iterations incorporate lightweight composites, improved corrosion resistance, and enhanced structural efficiency. Digital modeling and analysis tools are now used to optimize designs for specific applications, while maintaining the fundamental principles that made the original Bailey bridge so successful. Research continues into making these bridges even more portable, durable, and adaptable to various military and civilian needs.
The Bailey bridge represents a perfect fusion of engineering simplicity and practical effectiveness. Its contribution to military operations and civil engineering continues to be significant, more than 80 years after its invention. The principles behind its design remain relevant today, inspiring new generations of military engineers and demonstrating the enduring value of innovative yet practical solutions to complex problems.

A standard Bailey bridge can span up to 200 feet in its most reinforced configuration (triple-triple). However, the practical span length depends on the required load capacity and the specific configuration used.
A skilled military engineering team can construct a standard Bailey bridge in 4-6 hours for shorter spans (around 100 feet). However, longer spans or more complex configurations may require 24-48 hours for complete assembly.
The main advantages include rapid assembly without specialized equipment, portability, modular design allowing various configurations, and the ability to be dismantled and reused. These bridges can also be strengthened or modified after initial construction to meet changing requirements.
Yes, Bailey bridges are designed to operate in various weather conditions. However, extreme temperatures, high winds, and severe weather may affect construction timing and require additional safety measures during both assembly and use.
When properly maintained, a Bailey bridge can last 10-15 years in temporary installations. In permanent installations with regular maintenance and appropriate weather protection, they can last 25-30 years or more.
Do You Know The Structural Classifications of Rigid Frame Bridges?
What Are The Structural Characteristics of Steel Cable-Stayed Bridges and Steel Temporary Bridges?
Understanding the Sale of BS5400 Deck Steel Bailey Bridges in Papua New Guinea
Do You Know The Role of Steel Box Girders in Bridge Construction?
Understanding the AS5100 Design Load for Steel Truss Bridges in Railway Applications
The Lasting Impact of Bailey Bridges on Infrastructure Development
